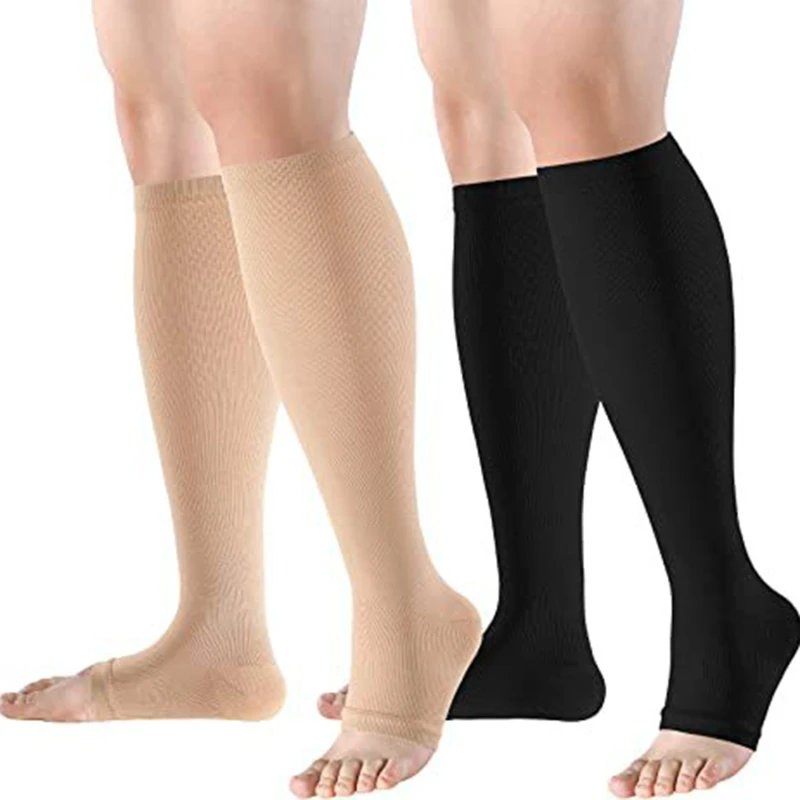
Compression stockings are commonly prescribed after surgery, especially following procedures that involve the legs, veins, or circulatory system. They are designed to promote blood circulation, reduce swelling, and lower the risk of blood clots. However, one of the most frequently asked questions by patients is: how long should you wear compression stockings after surgery? The answer can vary depending on the type of surgery, the individual’s health condition, and the advice of their healthcare provider. In this article, we will explore the key factors that determine the duration of wearing compression stockings post-surgery, the benefits they provide, and the considerations you should keep in mind when following your doctor’s recommendations.
1. The Purpose of Compression Stockings After Surgery
1.1. Improving Circulation and Preventing Blood Clots
Compression stockings are designed to apply gentle pressure to the legs, which helps enhance blood circulation. After surgery, especially if you’ve had a procedure involving your legs, veins, or even after general anesthesia, your circulation may be temporarily impaired. Reduced mobility and the natural healing process can increase the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), a condition where blood clots form in the deep veins, typically in the legs. Compression stockings help mitigate this risk by encouraging proper blood flow and reducing the likelihood of clot formation.
1.2. Reducing Swelling and Discomfort
Another important function of compression stockings is to reduce swelling, which is a common side effect of surgery. After an operation, especially if it involves the lower extremities, fluid may accumulate in the tissues, leading to swelling and discomfort. Compression stockings gently compress the tissues, helping the lymphatic and venous systems move the excess fluid away from the swollen areas and back into circulation. This can significantly reduce swelling, making the recovery process more comfortable for the patient.
1.3. Supporting Wound Healing
For certain types of surgery, such as those involving vein procedures (e.g., varicose vein treatments or leg surgery), compression stockings can help with wound healing. By promoting proper circulation, these stockings ensure that oxygen and nutrients effectively transport to the surgical site, which can speed up the healing process. Additionally, compression may prevent excessive movement of the area, reducing the risk of complications such as reopening the wound or infection.
2. How Long Should You Wear Compression Stockings After Surgery?
2.1. Immediate Post-Surgery Period
In the immediate post-surgery period, the duration for wearing compression stockings can depend on the nature of the surgery and the specific recommendations from your doctor. For most patients, compression stockings are recommended to be worn for 24 to 48 hours post-surgery, particularly if the surgery involves the legs, veins, or vascular system. During this time, the stockings help with initial swelling reduction, preventing clot formation, and promoting circulation during the early stages of recovery when mobility may be limited.
2.2. After Hospital Discharge: General Guidelines
Once you discharg from the hospital, the typical recommendation is to wear compression stockings for several weeks after surgery, especially if you are still recovering or have mobility issues. The exact time frame varies but generally ranges from 1 to 6 weeks. In the case of major surgeries, such as joint replacement or vascular surgery, compression stockings are often worn until the risk of blood clots significantly decreases, which can take several weeks.
Patients who had more minor or less invasive procedures may be advised to wear compression stockings for a shorter period, but it is important to continue using them for as long as your doctor recommends. This allows the body to adjust and heal fully without increased risks of complications such as DVT or swelling.
2.3. When to Stop Wearing Compression Stockings
Knowing when to stop wearing compression stockings is important for your recovery. Typically, once you regain normal mobility, and the swelling or risk of clot formation has reduced, you can begin tapering off the use of compression stockings. If your healthcare provider clears you for this, you may no longer need to wear them during the day, but they could still be recommended during periods of immobility, such as long flights or car trips, to help prevent any stagnation of blood flow. Some patients may instruct to continue wearing them during specific activities or at night if they are still experiencing significant swelling.
However, it’s crucial to follow the advice of your healthcare provider when deciding how long to wear them. For some, prolonged use (several months) might advis, particularly for people who are at higher risk of DVT or have poor circulation even after surgery. Therefore, it’s important to have regular follow-ups with your doctor to reassess your condition.

3. Types of Surgery That Typically Require Compression Stockings
3.1. Surgery Involving the Veins (Vein Surgery)
One of the most common types of surgery where compression stockings recommend is vein surgery, including treatments for varicose veins, venous insufficiency, or sclerotherapy. These procedures can disrupt normal blood flow, and compression stockings help ensure that blood continues to circulate effectively while reducing the risk of complications such as clotting or excessive swelling. After procedures like sclerotherapy or vein stripping, patients often instruct to wear compression stockings for a few weeks to support the veins’ recovery.
3.2. Orthopedic Surgery (Knee, Hip, or Leg Surgeries)
After orthopedic surgeries, such as knee replacements, hip replacements, or even fractures of the legs, compression stockings often prescrib to help with swelling and to reduce the risk of blood clots. These types of surgeries may require the patient to remain immobile for a significant period during recovery, which increases the risk of poor circulation and clot formation. Wearing compression stockings in the immediate and post-operative period helps mitigate these risks and supports the healing process by ensuring proper blood flow to the operated area.
3.3. Abdominal and Pelvic Surgeries
While not as common, some abdominal and pelvic surgeries (such as cesarean sections, hysterectomies, or surgeries for colon issues) may also require the use of compression stockings. These surgeries typically involve general anesthesia and can limit mobility, which places the patient at an increased risk of developing blood clots. Compression stockings are particularly beneficial in these cases, as they help ensure proper circulation while preventing deep vein thrombosis, especially in patients who remain in bed for extended periods.
4. Benefits and Risks of Wearing Compression Stockings
4.1. Benefits: Healing and Comfort
Compression stockings play a critical role in recovery by providing consistent, gentle pressure to the legs, which improves circulation and reduces swelling. In many cases, they are a critical component in post-surgical care, especially for surgeries involving the lower extremities. For patients recovering from joint replacements or vein procedures, wearing compression stockings can significantly reduce pain and discomfort by preventing excess fluid from accumulating in the tissues. Additionally, by supporting the veins, compression stockings can help prevent complications like blood clots, improving overall healing.
4.2. Risks and Considerations
While compression stockings are generally safe, there are some risks associate with improper use. If the stockings are too tight or incorrectly fitted, they could restrict circulation instead of promoting it, leading to discomfort or even more serious complications. It’s also important to ensure that you are following your doctor’s advice on when to wear the stockings and for how long. Overuse or misuse of compression stockings may lead to skin irritation, restricted blood flow, or worsening of underlying conditions. Always consult with your healthcare provider to make sure that the compression stockings you are using are appropriately fitted and used correctly.

5. How to Choose the Right Compression Stockings
5.1. Proper Fit and Compression Level
When selecting compression stockings, it’s essential to choose the correct fit and compression level to ensure effectiveness. Compression stockings are available in various sizes and pressure levels, typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). For post-surgical recovery, moderate compression levels (15-20 mmHg or 20-30 mmHg) usually recommend, but your healthcare provider will advise the most suitable level based on your specific surgery and recovery needs. A proper fit is crucial—too tight, and the stockings could hinder circulation; too loose, and they won’t provide the necessary pressure.
5.2. Material and Comfort
Compression stockings come in various materials, including nylon, spandex, and cotton blends. The material you choose will affect comfort, breathability, and durability. For long-term wear after surgery, breathable and moisture-wicking fabrics are preferable to keep your legs dry and prevent skin irritation. Many stockings are available in different lengths (knee-high, thigh-high, or full-leg), so be sure to choose the style that best fits your needs.
6. Conclusion
6.1. Follow Medical Advice for Optimal Recovery
In conclusion, compression stockings play a vital role in post-surgical recovery by promoting circulation, reducing swelling, and lowering the risk of blood clots. The length of time you should wear them after surgery depends on the type of procedure, your individual health status, and your doctor’s advice. While the typical wear time ranges from a few days to several weeks, some patients may need to continue using them for longer periods, especially if they are at a higher risk for complications.
As with any aspect of post-surgical care, it’s essential to follow your doctor’s specific recommendations regarding compression stockings. By doing so, you can ensure that your recovery is as smooth and comfortable as possible, minimizing risks and maximizing your chances of a successful, complication-free recovery.










